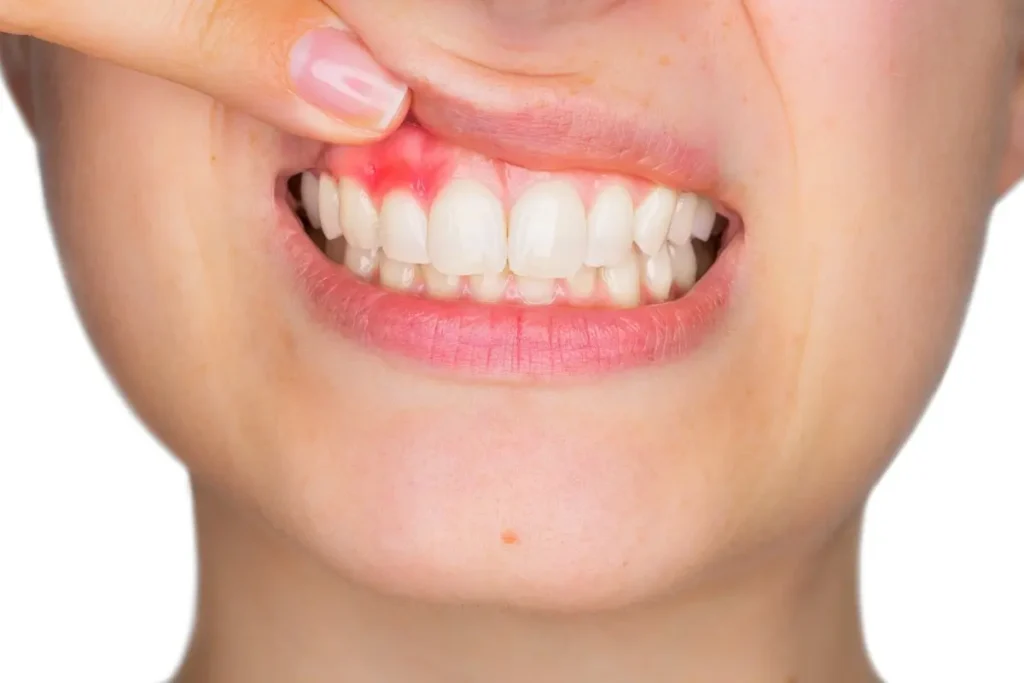
It is a worrying fact to realise that your gums are receding away around your teeth, and with good reason. Receding gums is not a point of cosmetic concern only, but a possible indicator of other underlying factors that affect your oral health in the long run.
When gum recession is not controlled, it not only exposes the sensitive root surfaces of your teeth, increases the risk of decay and sensitivity, but also leads to loss of teeth with time.
In case you have gum recession, a dentist will evaluate the cause of the recession and suggest ways of taking care of your smile.
Gums Recede Gradually — and Often Silently
Gum recession is a condition in which the tissue or soft tissue that surrounds your teeth shrinks back, exposing a greater part of the tooth or the root of the teeth. It may come gradually as time goes by, and thus, you may not realise it immediately. Common early signs include:
- Teeth that look longer than before
- Increased sensitivity to hot or cold stimuli
- Tender or bleeding gums
- Small notches near the gum line
These signs suggest that the gum tissue is no longer snug around your tooth, giving the formation of small pockets where bacteria are able to settle and cause further complications.
How Gum Recession Leads to Sensitivity and Decay
Receding of gum tissue exposes the root surfaces of your teeth. The root surface has nothing more than a thin cementum layer, in contrast with the crown of the tooth, which is enclosed by hard enamel. The layer does not provide much resistance to both temperature variations and bacterial infiltration.
This exposure can lead to:
Temperature and Touch Sensitivity
Exposed roots tend to respond to hot, cold, sweet or acidic food and beverages. You can have a sharp and painful sensation when eating or brushing.
Increased Risk of Decay
Since the root surface does not have hard-enamel, it becomes highly vulnerable to decay as soon as it is exposed. These areas can easily be penetrated and damaged by bacteria, making them more likely to develop cavities.
Progressive Tissue Loss
With the increase in recession, there can be deeper pockets between the tooth and gum. These crevices hold bacteria and tartar, which increase the tissue destruction and render daily brushing less effective in keeping the bacterial accumulation in check.
These complications illustrate the reason why it is important to detect and intervene at an early age despite the mild symptoms.
Common Causes of Gum Recession
Proper oral care and healthy gum tissue are helpful to protect your teeth; however, gum recession is caused by many factors. Some of the most common reasons are:
Periodontal (Gum) Disease
The first cause of recession is the bacterial infection of the gums. With the progression of the disease, it is what destroys gum tissue and the bone that holds your teeth.
Aggressive Brushing Habits
Excessive brushing or a toothbrush with hard bristles may grind away gum tissues, as well as the dental enamel. The risk is minimised by the use of a gentle technique and a soft brush.
Poor Oral Hygiene
Poor brushing and flossing results into the accumulation of plaque. The plaque becomes hard over a duration of time, forming tartar that may cause inflammation and recede the gums.
Teeth Grinding (Bruxism)
Clenching or grinding exerts too much strain on teeth and gums, which leads to gum recession and loss of bone that supports it.
Genetics and Thin Gum Tissue
Some individuals are inherently predisposed to recession because of genetic factors or having thinner gum tissue, which provides less resistance to bacteria.
Tobacco Use and Lifestyle Factors
Smoking and tobacco products limit the blood supply to the gum tissue, thereby hindering the healing process and risking recession.
Knowledge about the cause of your recession assists in the provision of the most appropriate treatment and prevention measures.
Treatment Options to Prevent Further Gum Loss
Even though once one has lost gum tissue, it does not grow back, there are multiple options available to slow down or prevent the recession process and take care of your oral health.
Improved Brushing and Flossing Techniques
Using a smooth-bristled toothbrush, a gentle form of technique, and flossing daily with soft bristles removes the harmful plaque and lowers the gum tissue trauma.
Professional Dental Cleanings
Visiting the dentist in sydney regularly will enable your dentist to remove tartar or hardened plaque and monitor the early stages of gum disease.
Scaling and Root Planing
In moderate cases, your dentist might prescribe a deep cleaning known as scaling and root planing to help remove the bacteria under the gumline as well as smooth the tooth root surfaces.
Gum Grafting and Surgical Options
In more advanced stages of significant tissue loss, gum grafting may be used to safeguard exposed roots and to enhance functionality and appearance.
Treatment decisions depend on the severity of recession, your overall oral health and your dentist’s evaluation.
Wrap-Up: Protecting Your Gums Before It’s Too Late
Gum recession is not all about the appearance of the teeth. It concerns the smile’s longevity and stability. The more exposed the roots, the more decay, sensitivity, and consequent loss of teeth should the recession be unchecked.
Daily oral care, periodic dental check-ups and control at the onset of recession can help a great deal. This will benefit you by visiting a dental clinic in Sydney at an early age and establishing the cause, yielding personal treatment options and safeguarding your gums and teeth against any future harm.
FAQs
Can receding gums grow back naturally?
No. Once gum tissue is lost, it doesn’t grow back naturally. However, treatments like scaling and root planing or gum grafts can help protect exposed areas and prevent progression.
What do receding gums look like?
Signs include teeth appearing longer than before, increased sensitivity, tiny notches at the gumline, and visible roots in advanced cases.
Are receding gums always painful?
Not always. Some people experience sensitivity or discomfort, while others notice visual changes without pain. Sensitivity often increases as more roots become exposed.
Can brushing too hard really cause gum recession?
Yes. Using excessive force or a hard-bristled toothbrush can damage gum tissue over time and contribute to recession. A soft brush and gentle technique help reduce this risk.
How often should I see a dentist to check for gum recession?
Routine dental check-ups every six months, or more frequently if recommended, help catch early signs of gum recession and allow timely intervention.
Does gum disease always lead to gum recession?
Gum disease is a major cause of recession, but not everyone with gum disease will necessarily experience significant recession. Early detection and care reduce the risk.
Taking receding gums seriously and seeking professional advice early can make a huge difference to your long-term oral health and comfort.
Also Read